Apomorphine (T3D2867)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:28 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:52 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2867 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Apomorphine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | A derivative of morphine that is a dopamine D2 agonist. It is a powerful emetic and has been used for that effect in acute poisoning. It has also been used in the diagnosis and treatment of parkinsonism, but its adverse effects limit its use. [PubChem] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
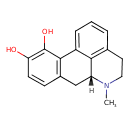
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C17H17NO2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 267.322 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.126 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 41372-20-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (9R)-10-methyl-10-azatetracyclo[7.7.1.0²,⁷.0¹³,¹⁷]heptadeca-1(16),2(7),3,5,13(17),14-hexaene-3,4-diol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | apomorphine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@]12CC3=C(C(O)=C(O)C=C3)C3=CC=CC(CCN1C)=C23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C17H17NO2/c1-18-8-7-10-3-2-4-12-15(10)13(18)9-11-5-6-14(19)17(20)16(11)12/h2-6,13,19-20H,7-9H2,1H3/t13-/m1/s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=VMWNQDUVQKEIOC-CYBMUJFWSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aporphines. These are quinoline alkaloids containing the dibenzo[de,g]quinoline ring system or a dehydrogenated derivative thereof. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Aporphines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Aporphines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | 100% following subcutaneous administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The precise mechanism of action of apomorphine as a treatment for Parkinson's disease is unknown, although it is believed to be due to stimulation of post-synaptic dopamine D2-type receptors within the brain. Apomorphine has been shown to improve motor function in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. In particular, apomorphine attenuates the motor deficits induced by lesions in the ascending nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in primates. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Hepatic Half Life: 40 minutes (range 30 - 60 minutes) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 0.6 mmoles/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For the acute, intermittent treatment of hypomobility, off episodes (end-of-dose wearing off and unpredictable on/off episodes) associated with advanced Parkinson's disease. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00714 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14852 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 6005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 5783 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 48538 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Apomorphine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Apomorphine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Narayanasamy Gurusamy, “Process for Making Apomorphine and Apocodeine.” U.S. Patent US20100228032, issued September 09, 2010. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.00062 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0036 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.026 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.028 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.032 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0416 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0419 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.05 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.053 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.098 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.244 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | >0.217 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Dissociation | 0.00066 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Dissociation | 0.024 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Dissociation | 0.127 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Yamada S, Harano M, Annoh N, Nakamura K, Tanaka M: Involvement of serotonin 2A receptors in phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats. Biol Psychiatry. 1999 Sep 15;46(6):832-8. [10494453 ]
- Kim HJ, Koh PO, Kang SS, Paik WY, Choi WS: The localization of dopamine D2 receptor mRNA in the human placenta and the anti-angiogenic effect of apomorphine in the chorioallantoic membrane. Life Sci. 2001 Jan 19;68(9):1031-40. [11212866 ]
- Yamada S: [Disruption of prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle as an animal model for schizophrenia]. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2000 Oct;20(4):131-9. [11215397 ]
- Berlin I, de Brettes B, Aymard G, Diquet B, Arnulf I, Puech AJ: Dopaminergic drug response and the genotype (Taq IA polymorphism) of the dopamine D2 receptor. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000 Mar;3(1):35-43. [11343576 ]
- Lucht MJ, Kuehn KU, Schroeder W, Armbruster J, Abraham G, Schattenberg A, Gaensicke M, Barnow S, Tretzel H, Herrmann FH, Freyberger HJ: Influence of the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) exon 8 genotype on efficacy of tiapride and clinical outcome of alcohol withdrawal. Pharmacogenetics. 2001 Nov;11(8):647-53. [11692072 ]
- Ramsby S, Neumeyer JL, Grigoriadis D, Seeman P: 2-Haloaporphines as potent dopamine agonists. J Med Chem. 1989 Jun;32(6):1198-201. [2524592 ]
- Brusniak MY, Pearlman RS, Neve KA, Wilcox RE: Comparative molecular field analysis-based prediction of drug affinities at recombinant D1A dopamine receptors. J Med Chem. 1996 Feb 16;39(4):850-9. [8632409 ]
- Pettersson F, Ponten H, Waters N, Waters S, Sonesson C: Synthesis and evaluation of a set of 4-phenylpiperidines and 4-phenylpiperazines as D2 receptor ligands and the discovery of the dopaminergic stabilizer 4-[3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1-propylpiperidine (huntexil, pridopidine, ACR16). J Med Chem. 2010 Mar 25;53(6):2510-20. doi: 10.1021/jm901689v. [20155917 ]
- Patel MV, Kolasa T, Mortell K, Matulenko MA, Hakeem AA, Rohde JJ, Nelson SL, Cowart MD, Nakane M, Miller LN, Uchic ME, Terranova MA, El-Kouhen OF, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Namovic MT, Hollingsworth PR, Chang R, Martino BR, Wetter JM, Marsh KC, Martin R, Darbyshire JF, Gintant G, Hsieh GC, Moreland RB, Sullivan JP, Brioni JD, Stewart AO: Discovery of 3-methyl-N-(1-oxy-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-2'H-[2,4'-bipyridine]-1'-ylmethyl)benzam ide (ABT-670), an orally bioavailable dopamine D4 agonist for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Med Chem. 2006 Dec 14;49(25):7450-65. [17149874 ]
- Lin CH, Haadsma-Svensson SR, Lahti RA, McCall RB, Piercey MF, Schreur PJ, Von Voigtlander PF, Smith MW, Chidester CG: Centrally acting serotonergic and dopaminergic agents. 1. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 2,3,3a,4,5,9b-hexahydro-1H-benz[e]indole derivatives. J Med Chem. 1993 Apr 16;36(8):1053-68. [8097537 ]
- Lin CH, Haadsma-Svensson SR, Phillips G, Lahti RA, McCall RB, Piercey MF, Schreur PJ, Von Voigtlander PF, Smith MW, Chidester CG: Centrally acting serotonergic and dopaminergic agents. 2. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 2,3,3a,4,9,9a-hexahydro-1H-benz[f]indole derivatives. J Med Chem. 1993 Apr 16;36(8):1069-83. [8097538 ]
- Wright JL, Caprathe BW, Downing DM, Glase SA, Heffner TG, Jaen JC, Johnson SJ, Kesten SR, MacKenzie RG, Meltzer LT, et al.: The discovery and structure-activity relationships of 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-phenyl-1-[(arylcyclohexenyl)alkyl]pyridines. Dopamine autoreceptor agonists and potential antipsychotic agents. J Med Chem. 1994 Oct 14;37(21):3523-33. [7932581 ]
- Sipos A, Csutoras C, Berenyi S, Uustare A, Rinken A: Synthesis and neuropharmacological characterization of 2-O-substituted apomorphines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Apr 15;16(8):4563-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.038. Epub 2008 Feb 15. [18313931 ]
- Linnanen T, Brisander M, Unelius L, Sundholm G, Hacksell U, Johansson AM: Derivatives of (R)-1,11-methyleneaporphine: synthesis, structure, and interactions with G-protein coupled receptors. J Med Chem. 2000 Apr 6;43(7):1339-49. [10753471 ]
- Hedberg MH, Johansson AM, Nordvall G, Yliniemela A, Li HB, Martin AR, Hjorth S, Unelius L, Sundell S, Hacksell U: (R)-11-hydroxy- and (R)-11-hydroxy-10-methylaporphine: synthesis, pharmacology, and modeling of D2A and 5-HT1A receptor interactions. J Med Chem. 1995 Feb 17;38(4):647-58. [7861413 ]
- Hedberg MH, Jansen JM, Nordvall G, Hjorth S, Unelius L, Johansson AM: 10-substituted 11-oxygenated (R)-aporphines: synthesis, pharmacology, and modeling of 5-HT1A receptor interactions. J Med Chem. 1996 Aug 30;39(18):3491-502. [8784447 ]
- Hedberg MH, Linnanen T, Jansen JM, Nordvall G, Hjorth S, Unelius L, Johansson AM: 11-substituted (R)-aporphines: synthesis, pharmacology, and modeling of D2A and 5-HT1A receptor interactions. J Med Chem. 1996 Aug 30;39(18):3503-13. [8784448 ]
- Linnanen T, Brisander M, Unelius L, Rosqvist S, Nordvall G, Hacksell U, Johansson AM: Atropisomeric derivatives of 2',6'-disubstituted (R)-11-phenylaporphine: selective serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 2001 Apr 26;44(9):1337-40. [11311055 ]
- Reinart-Okugbeni R, Ausmees K, Kriis K, Werner F, Rinken A, Kanger T: Chemoenzymatic synthesis and evaluation of 3-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane derivatives as dopaminergic ligands. Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Sep;55:255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.07.025. Epub 2012 Jul 24. [22846798 ]
- Reinart-Okugbeni R, Vonk A, Uustare A, Gyulai Z, Sipos A, Rinken A: 1-substituted apomorphines as potent dopamine agonists. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Jul 15;21(14):4143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.05.014. Epub 2013 May 16. [23727194 ]
- Liu Z, Chen X, Yu L, Zhen X, Zhang A: Synthesis and pharmacological investigation of novel 2-aminothiazole-privileged aporphines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jul 15;16(14):6675-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.05.077. Epub 2008 Jun 5. [18562201 ]
- Sonesson C, Lin CH, Hansson L, Waters N, Svensson K, Carlsson A, Smith MW, Wikstrom H: Substituted (S)-phenylpiperidines and rigid congeners as preferential dopamine autoreceptor antagonists: synthesis and structure-activity relationships. J Med Chem. 1994 Aug 19;37(17):2735-53. [8064801 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21728
- Molecular Weight:
- 49292.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0046 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.072 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.29 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.37154 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.4 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.65 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.66 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.68 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Dissociation | 0.68 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Guo H, Tang Z, Yu Y, Xu L, Jin G, Zhou J: Apomorphine induces trophic factors that support fetal rat mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in cultures. Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Nov;16(10):1861-70. [12453049 ]
- Brusniak MY, Pearlman RS, Neve KA, Wilcox RE: Comparative molecular field analysis-based prediction of drug affinities at recombinant D1A dopamine receptors. J Med Chem. 1996 Feb 16;39(4):850-9. [8632409 ]
- Sromek AW, Si YG, Zhang T, George SR, Seeman P, Neumeyer JL: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of N-Fluoroalkyl and 2-Fluoroalkoxy Substituted Aporphines: Potential PET Ligands for Dopamine D(2) Receptors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011 Mar 10;2(3):189-194. [21666830 ]
- Herm L, Berenyi S, Vonk A, Rinken A, Sipos A: N-Substituted-2-alkyl- and 2-arylnorapomorphines: novel, highly active D2 agonists. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Jul 1;17(13):4756-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.04.047. Epub 2009 May 3. [19454369 ]
- Reinart R, Gyulai Z, Berenyi S, Antus S, Vonk A, Rinken A, Sipos A: New 2-thioether-substituted apomorphines as potent and selective dopamine D(2) receptor agonists. Eur J Med Chem. 2011 Jul;46(7):2992-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.04.028. Epub 2011 Apr 22. [21550699 ]
- Liu Z, Chen X, Yu L, Zhen X, Zhang A: Synthesis and pharmacological investigation of novel 2-aminothiazole-privileged aporphines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jul 15;16(14):6675-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.05.077. Epub 2008 Jun 5. [18562201 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- Toll L, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Polgar WE, Brandt SR, Adapa ID, Rodriguez L, Schwartz RW, Haggart D, O'Brien A, White A, Kennedy JM, Craymer K, Farrington L, Auh JS: Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res Monogr. 1998 Mar;178:440-66. [9686407 ]
- Reinart-Okugbeni R, Ausmees K, Kriis K, Werner F, Rinken A, Kanger T: Chemoenzymatic synthesis and evaluation of 3-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane derivatives as dopaminergic ligands. Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Sep;55:255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.07.025. Epub 2012 Jul 24. [22846798 ]
- Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O'Dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HH, Niznik HB: Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614-9. [1826762 ]
- Ryman-Rasmussen JP, Nichols DE, Mailman RB: Differential activation of adenylate cyclase and receptor internalization by novel dopamine D1 receptor agonists. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Oct;68(4):1039-48. Epub 2005 Jun 28. [15985612 ]
- General Function:
- Sh3 domain binding
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Its activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Modulates the circadian rhythm of contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of NPAS2 in the retinal ganglion cells (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- DRD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P21917
- Molecular Weight:
- 48359.86 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0089 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Mansbach RS, Brooks EW, Sanner MA, Zorn SH: Selective dopamine D4 receptor antagonists reverse apomorphine-induced blockade of prepulse inhibition. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1998 Jan;135(2):194-200. [9497025 ]
- Sanner MA, Chappie TA, Dunaiskis AR, Fliri AF, Desai KA, Zorn SH, Jackson ER, Johnson CG, Morrone JM, Seymour PA, Majchrzak MJ, Faraci WS, Collins JL, Duignan DB, Prete Di CC, Lee JS, Trozzi A: Synthesis, SAR and pharmacology of CP-293,019: a potent, selective dopamine D4 receptor antagonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998 Apr 7;8(7):725-30. [9871530 ]
- Succu S, Sanna F, Melis T, Boi A, Argiolas A, Melis MR: Stimulation of dopamine receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats induces penile erection and increases extra-cellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens: Involvement of central oxytocin. Neuropharmacology. 2007 Mar;52(3):1034-43. Epub 2006 Dec 11. [17164075 ]
- Boeckler F, Russig H, Zhang W, Lober S, Schetz J, Hubner H, Ferger B, Gmeiner P, Feldon J: FAUC 213, a highly selective dopamine D4 receptor full antagonist, exhibits atypical antipsychotic properties in behavioural and neurochemical models of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Aug;175(1):7-17. Epub 2004 Mar 6. [15007532 ]
- Melis MR, Succu S, Sanna F, Melis T, Mascia MS, Enguehard-Gueiffier C, Hubner H, Gmeiner P, Gueiffier A, Argiolas A: PIP3EA and PD-168077, two selective dopamine D4 receptor agonists, induce penile erection in male rats: site and mechanism of action in the brain. Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Oct;24(7):2021-30. [17067298 ]
- Patel MV, Kolasa T, Mortell K, Matulenko MA, Hakeem AA, Rohde JJ, Nelson SL, Cowart MD, Nakane M, Miller LN, Uchic ME, Terranova MA, El-Kouhen OF, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Namovic MT, Hollingsworth PR, Chang R, Martino BR, Wetter JM, Marsh KC, Martin R, Darbyshire JF, Gintant G, Hsieh GC, Moreland RB, Sullivan JP, Brioni JD, Stewart AO: Discovery of 3-methyl-N-(1-oxy-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-2'H-[2,4'-bipyridine]-1'-ylmethyl)benzam ide (ABT-670), an orally bioavailable dopamine D4 agonist for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Med Chem. 2006 Dec 14;49(25):7450-65. [17149874 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.296 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.534 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 4.929 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Linnanen T, Brisander M, Unelius L, Sundholm G, Hacksell U, Johansson AM: Derivatives of (R)-1,11-methyleneaporphine: synthesis, structure, and interactions with G-protein coupled receptors. J Med Chem. 2000 Apr 6;43(7):1339-49. [10753471 ]
- Linnanen T, Brisander M, Unelius L, Rosqvist S, Nordvall G, Hacksell U, Johansson AM: Atropisomeric derivatives of 2',6'-disubstituted (R)-11-phenylaporphine: selective serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 2001 Apr 26;44(9):1337-40. [11311055 ]
- Moon MW, Morris JK, Heier RF, Chidester CG, Hoffmann WE, Piercey MF, Althaus JS, Von Voigtlander PF, Evans DL, Figur LM, et al.: Dopaminergic and serotonergic activities of imidazoquinolinones and related compounds. J Med Chem. 1992 Mar 20;35(6):1076-92. [1348089 ]
- Toll L, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Polgar WE, Brandt SR, Adapa ID, Rodriguez L, Schwartz RW, Haggart D, O'Brien A, White A, Kennedy JM, Craymer K, Farrington L, Auh JS: Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res Monogr. 1998 Mar;178:440-66. [9686407 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Promotes cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- DRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P35462
- Molecular Weight:
- 44224.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0026 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0078 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.01 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Sromek AW, Si YG, Zhang T, George SR, Seeman P, Neumeyer JL: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of N-Fluoroalkyl and 2-Fluoroalkoxy Substituted Aporphines: Potential PET Ligands for Dopamine D(2) Receptors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011 Mar 10;2(3):189-194. [21666830 ]
- Wright JL, Caprathe BW, Downing DM, Glase SA, Heffner TG, Jaen JC, Johnson SJ, Kesten SR, MacKenzie RG, Meltzer LT, et al.: The discovery and structure-activity relationships of 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-phenyl-1-[(arylcyclohexenyl)alkyl]pyridines. Dopamine autoreceptor agonists and potential antipsychotic agents. J Med Chem. 1994 Oct 14;37(21):3523-33. [7932581 ]
- Reinart-Okugbeni R, Ausmees K, Kriis K, Werner F, Rinken A, Kanger T: Chemoenzymatic synthesis and evaluation of 3-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane derivatives as dopaminergic ligands. Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Sep;55:255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.07.025. Epub 2012 Jul 24. [22846798 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD5
- Uniprot ID:
- P21918
- Molecular Weight:
- 52950.5 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.01479 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| Inhibitory | 0.363 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O'Dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HH, Niznik HB: Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614-9. [1826762 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, nociceptive processing, pain perception, mood and behavior. Besides, plays a role in vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P28222
- Molecular Weight:
- 43567.535 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 2.95121 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity. May also play a role in regulating the release of other neurotransmitters. May play a role in vasoconstriction.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P28221
- Molecular Weight:
- 41906.38 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 1.23027 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.12023 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various ergot alkaloid derivatives and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release, 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and in the regulation of extracellular dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels, and thereby affects neural activity. May play a role in the perception of pain. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including impulsive behavior. Required for normal proliferation of embryonic cardiac myocytes and normal heart development. Protects cardiomyocytes against apoptosis. Plays a role in the adaptation of pulmonary arteries to chronic hypoxia. Plays a role in vasoconstriction. Required for normal osteoblast function and proliferation, and for maintaining normal bone density. Required for normal proliferation of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the intestine.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P41595
- Molecular Weight:
- 54297.41 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.13183 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.10233 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Thioesterase binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08913
- Molecular Weight:
- 48956.275 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.14125 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Epinephrine binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is clonidine > norepinephrine > epinephrine = oxymetazoline > dopamine > p-tyramine = phenylephrine > serotonin > p-synephrine / p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > chlorpromazine > phentolamine > mianserine > spiperone > prazosin > alprenolol > propanolol > pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P18089
- Molecular Weight:
- 49565.8 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.06607 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P18825
- Molecular Weight:
- 49521.585 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.03631 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kvernmo T, Houben J, Sylte I: Receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopaminergic agonists. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(12):1049-67. [18691132 ]
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Protein heterodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine (PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P35368
- Molecular Weight:
- 56835.375 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.67608 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Alpha1-adrenergic receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its effect through the influx of extracellular calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P25100
- Molecular Weight:
- 60462.205 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.06457 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor signaling protein activity
- Specific Function:
- Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. This receptor binds epinephrine and norepinephrine with approximately equal affinity. Mediates Ras activation through G(s)-alpha- and cAMP-mediated signaling.
- Gene Name:
- ADRB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08588
- Molecular Weight:
- 51322.1 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | >10 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A: Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804. [12388666 ]
- General Function:
- Clathrin light chain binding
- Specific Function:
- Interacts with clathrin light chain A and stimulates clathrin self-assembly and clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
- Gene Name:
- CALY
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NYX4
- Molecular Weight:
- 23433.49 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- General Function:
- Opioid receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Functions in lipid transport from the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in a wide array of cellular functions probably through regulation of the biogenesis of lipid microdomains at the plasma membrane. Involved in the regulation of different receptors it plays a role in BDNF signaling and EGF signaling. Also regulates ion channels like the potassium channel and could modulate neurotransmitter release. Plays a role in calcium signaling through modulation together with ANK2 of the ITP3R-dependent calcium efflux at the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in several other cell functions including proliferation, survival and death. Originally identified for its ability to bind various psychoactive drugs it is involved in learning processes, memory and mood alteration (PubMed:16472803, PubMed:9341151). Necessary for proper mitochondrial axonal transport in motor neurons, in particular the retrograde movement of mitochondria (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SIGMAR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99720
- Molecular Weight:
- 25127.52 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | >10 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
| IC50 | >31 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50001955 |
References
- Kimes AS, Wilson AA, Scheffel U, Campbell BG, London ED: Radiosynthesis, cerebral distribution, and binding of [125I]-1-(p-iodophenyl)-3-(1-adamantyl)guanidine, a ligand for sigma binding sites. J Med Chem. 1992 Dec 11;35(25):4683-9. [1469697 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.00 uM | NVS_NR_hER | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.12 uM | ATG_PXR_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 1.54 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.15 uM | NVS_NR_hPXR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcription factor. Key regulator of lipid metabolism. Activated by the endogenous ligand 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine (16:0/18:1-GPC). Activated by oleylethanolamide, a naturally occurring lipid that regulates satiety. Receptor for peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the ACOX1 and P450 genes. Transactivation activity requires heterodimerization with RXRA and is antagonized by NR2C2. May be required for the propagation of clock information to metabolic pathways regulated by PER2.
- Gene Name:
- PPARA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07869
- Molecular Weight:
- 52224.595 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.01 uM | ATG_PPRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.26 uM | NVS_NR_hPPARa | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription regulatory region dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcriptional activator. Binds to the XRE promoter region of genes it activates. Activates the expression of multiple phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes (such as the CYP1A1 gene). Mediates biochemical and toxic effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Involved in cell-cycle regulation. Likely to play an important role in the development and maturation of many tissues. Regulates the circadian clock by inhibiting the basal and circadian expression of the core circadian component PER1. Inhibits PER1 by repressing the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer mediated transcriptional activation of PER1.
- Gene Name:
- AHR
- Uniprot ID:
- P35869
- Molecular Weight:
- 96146.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.50 uM | ATG_Ahr_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.92 uM | Tox21_AhR | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Cholesterol binding
- Specific Function:
- Can bind protoporphyrin IX and may play a role in the transport of porphyrins and heme (By similarity). Promotes the transport of cholesterol across mitochondrial membranes and may play a role in lipid metabolism (PubMed:24814875), but its precise physiological role is controversial. It is apparently not required for steroid hormone biosynthesis. Was initially identified as peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor; can also bind isoquinoline carboxamides (PubMed:1847678).
- Gene Name:
- TSPO
- Uniprot ID:
- P30536
- Molecular Weight:
- 18827.81 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.71 uM | NVS_MP_hPBR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for retinoic acid. Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence of ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. Required for limb bud development. In concert with RARA or RARB, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- RARG
- Uniprot ID:
- P13631
- Molecular Weight:
- 50341.405 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.24 uM | ATG_DR5_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 2.42 uM | ATG_RARg_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear phosphoprotein which forms a tight but non-covalently linked complex with the JUN/AP-1 transcription factor. In the heterodimer, FOS and JUN/AP-1 basic regions each seems to interact with symmetrical DNA half sites. On TGF-beta activation, forms a multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP1/SMAD-binding site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated signaling. Has a critical function in regulating the development of cells destined to form and maintain the skeleton. It is thought to have an important role in signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. In growing cells, activates phospholipid synthesis, possibly by activating CDS1 and PI4K2A. This activity requires Tyr-dephosphorylation and association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Gene Name:
- FOS
- Uniprot ID:
- P01100
- Molecular Weight:
- 40694.855 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.73 uM | ATG_AP_1_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii distal enhancer sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Transcription activator that binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements in the promoter regions of target genes. Important for the coordinated up-regulation of genes in response to oxidative stress. May be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region.
- Gene Name:
- NFE2L2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16236
- Molecular Weight:
- 67825.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.13 uM | ATG_NRF2_ARE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]