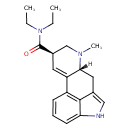
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (T3D3582)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-08-12 19:36:03 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:10 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3582 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Lysergic Acid Diethylamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Lysergic acid diethylamide, abbreviated LSD or LSD-25, also known as lysergide and colloquially as acid, is a semisynthetic psychedelic drug of the ergoline family. It was first synthesized by Albert Hofmann in 1938 from ergot, a grain fungus that typically grows on rye. LSD is non-addictive and non-toxic. It is well known for its psychological effects which can include altered thinking processes, closed and open eye visuals, synaesthesia, a sense of time distortion, ego death and spiritual experiences, as well as for its key role in 1960s counterculture. It is used mainly by psychonauts as an entheogen, recreational drug and as an agent in psychedelic therapy. (9). Debate continues over the nature and causes of chronic flashbacks. Explanations in terms of LSD physically remaining in the body for months or years after consumption have been discounted by experimental evidence. Some say Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) is a manifestation of post-traumatic stress disorder, not related to the direct action of LSD on brain chemistry, and varies according to the susceptibility of the individual to the disorder. Many emotionally intense experiences can lead to flashbacks when a person is reminded acutely of the original experience. However, not all published case reports of chronic flashbacks appear to describe an anxious hyper-vigilant state reminiscent of post-traumatic stress disorder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C20H25N3O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 323.432 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 323.200 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 50-37-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (4R,7R)-N,N-diethyl-6-methyl-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0²,⁷.0¹²,¹⁶]hexadeca-1(16),2,9,12,14-pentaene-4-carboxamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | lysergic acid diethylamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CN(C)[C@]2([H])CC3=CNC4=CC=CC(=C34)C2=C1)C(=O)N(CC)CC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H25N3O/c1-4-23(5-2)20(24)14-9-16-15-7-6-8-17-19(15)13(11-21-17)10-18(16)22(3)12-14/h6-9,11,14,18,21H,4-5,10,12H2,1-3H3/t14-,18-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=VAYOSLLFUXYJDT-RDTXWAMCSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as lysergic acids and derivatives. These are alkaloids with a structure based on the lysergic acid skeleton. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Ergoline and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Lysergic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Lysergic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Rapidly absorbed. Oral (usually on a substrate such as absorbent blotter paper, a sugar cube, or gelatin) (9); Intramuscular or intravenous injection (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | LSD preferentially inhibits serotonergic cell firing by acting as an agonist at the 5-HT1A receptors in the raphe nuclei, locus coeruleus, and cortex. It also acts as a partial agonist on the postsynaptic 5-HT1A site and has high affinity for the other 5-HT1 subtypes 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT1E. LSD's hallucinogenic effects are caused by its ability to act as a partial agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor, especially on neocortical pyramidal cells. Activation of 5-HT2A also leads to increased cortical glutamate levels. Effects of LSD on 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors have also been described, but their significance remains uncertain. In addition, LSD shows agonistic and antagonistic behavior at the central dopamine D1 and D2-receptors. (9, 8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | LSD's effects normally last from 6 - 12 hours depending on dosage, tolerance, body weight and age. Its half-life in humans is 175 min. It is metabolized in the liver by NADH-dependent microsomal enzymes and its metabolites may be quantified in the urine. The major metabolite is 2-oxy-3-hydroxy-LSD. Other metabolites include 2-oxy-LSD, LAE, nor-LSD, di-hydroxy-LSD, 13- and 14-hydroxy-LSD as glucoronides, lysergic acid ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamide (LEO), and trioxylated LSD. (9, 8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Estimates for the lethal dosage (LD50) of LSD range from 200 ug/kg to more than 1 mg/kg of human body mass, though most sources report that there are no known human cases of such an overdose. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | LSD has not been known to cause death on its own. (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Lysergic acid diethylamide, is one of the most widely known psychedelic drugs. It has been used mainly as an entheogen, a tool to supplement various practices for transcendence, including meditation, psychonautics, art projects, and (formerly legal) psychedelic therapy, and as a recreational drug. Formally, LSD is classified as a hallucinogen of the psychedelic type. (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Chronic effects of LSD toxicity include flashbacks, psychosis, and exacerbation of latent mental disorders, particularly schizophrenia. Overdosage can result in “bad trips” that are characterized by intense anxiety, combativeness, confusion, and panic attacks. LSD is not considered to be addictive, and withdrawal syndrome are absent. Because of its relatively high therapeutic index, no deaths have been directly attributed to LSD use alone. (7, 9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | LSD reliably causes pupil dilation, reduced appetite, and wakefulness. Other physical reactions to LSD are highly variable and nonspecific, and some of these reactions may be secondary to the psychological effects of LSD. The following symptoms have been reported: numbness, weakness, nausea, hypothermia or hyperthermia, elevated blood sugar, goose bumps, increase in heart rate, jaw clenching, perspiration, saliva production, mucus production, sleeplessness, hyperreflexia, and tremors. LSD also causes expansion and an altered experience of senses, emotions, memories, time, and awareness. These psychological effects (colloquially called a "trip") vary greatly from person to person. Visual effects may include morphing objects, illusion of movement of static surfaces, after image-like trails of moving objects, the appearance of moving colored geometric patterns, an intensification of colors and brightness, new textures on objects, blurred vision, and shape suggestibility. The auditory effects of LSD may include echo-like distortions of sounds, changes in ability to discern concurrent auditory stimuli, and a general intensification of the experience of music. Higher doses often cause intense and fundamental distortions of sensory perception such as synaesthesia, the experience of additional spatial or temporal dimensions, and temporary dissociation. (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Adverse effects of psychotropics are often treated with fast-acting benzodiazepines like diazepam or triazolam that have calming and antianxiety effects but do not directly affect the specific actions of psychotropics. Theoretically, specific 5-HT2A receptor antagonists, which most commonly means atypical antipsychotics (quetiapine, olanzapine, risperidone, etc.) or other 5-HT2A antagonist such as trazodone or mirtazapine, would be direct antidotes, although some anecdotal reports claim otherwise. (1, 9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB04829 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 5761 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL263881 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 5558 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07542 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 6605 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Lysergic Acid Diethylamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Lysergic_acid_diethylamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Jean-Luc Henri Sigier Emmanuel, “Device for maintaining the inner surface of gun barrels and method for producing same.” U.S. Patent US5657570, issued September, 1918. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D3582.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0011 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- Chambers JJ, Parrish JC, Jensen NH, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM, Marona-Lewicka D, Nichols DE: Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of a series of geometrically constrained 5-HT(2A/2C) receptor ligands. J Med Chem. 2003 Jul 31;46(16):3526-35. [12877591 ]
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0026 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0027 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0031 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0035 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
| Inhibitory | 0.004 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
| Inhibitory | 0.0052 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas SP, Chemel BR, Rehder KS, Zhong D, Lewin AH: High specific activity tritium-labeled N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO): a high-affinity 5-HT2A receptor-selective agonist radioligand. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jun 1;16(11):6116-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.050. Epub 2008 Apr 25. [18468904 ]
- Egan C, Grinde E, Dupre A, Roth BL, Hake M, Teitler M, Herrick-Davis K: Agonist high and low affinity state ratios predict drug intrinsic activity and a revised ternary complex mechanism at serotonin 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors. Synapse. 2000 Feb;35(2):144-50. [10611640 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. It has a high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs (By similarity). Controls pyramidal neurons migration during corticogenesis, through the regulation of CDK5 activity (By similarity). Is an activator of TOR signaling (PubMed:23027611).
- Gene Name:
- HTR6
- Uniprot ID:
- P50406
- Molecular Weight:
- 46953.625 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0069 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- van Loevezijn A, Venhorst J, Iwema Bakker WI, de Korte CG, de Looff W, Verhoog S, van Wees JW, van Hoeve M, van de Woestijne RP, van der Neut MA, Borst AJ, van Dongen MJ, de Bruin NM, Keizer HG, Kruse CG: N'-(arylsulfonyl)pyrazoline-1-carboxamidines as novel, neutral 5-hydroxytryptamine 6 receptor (5-HT(6)R) antagonists with unique structural features. J Med Chem. 2011 Oct 27;54(20):7030-54. doi: 10.1021/jm200466r. Epub 2011 Sep 26. [21866910 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity. May also play a role in regulating the release of other neurotransmitters. May play a role in vasoconstriction.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P28221
- Molecular Weight:
- 41906.38 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0039 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various alkaloids and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1E
- Uniprot ID:
- P28566
- Molecular Weight:
- 41681.57 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.093 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various ergot alkaloid derivatives and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release, 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and in the regulation of extracellular dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels, and thereby affects neural activity. May play a role in the perception of pain. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including impulsive behavior. Required for normal proliferation of embryonic cardiac myocytes and normal heart development. Protects cardiomyocytes against apoptosis. Plays a role in the adaptation of pulmonary arteries to chronic hypoxia. Plays a role in vasoconstriction. Required for normal osteoblast function and proliferation, and for maintaining normal bone density. Required for normal proliferation of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the intestine.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P41595
- Molecular Weight:
- 54297.41 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.03 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- Blanpain C, Le Poul E, Parma J, Knoop C, Detheux M, Parmentier M, Vassart G, Abramowicz MJ: Serotonin 5-HT(2B) receptor loss of function mutation in a patient with fenfluramine-associated primary pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2003 Dec 1;60(3):518-28. [14659797 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- HTR5A
- Uniprot ID:
- P47898
- Molecular Weight:
- 40254.69 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.009 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- HTR7
- Uniprot ID:
- P34969
- Molecular Weight:
- 53554.43 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0066 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD5
- Uniprot ID:
- P21918
- Molecular Weight:
- 52950.5 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.34 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.12 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for ergot alkaloid derivatives, various anxiolytic and antidepressant drugs and other psychoactive substances, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity. Arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Regulates the release of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, nociceptive processing, pain perception, mood and behavior. Besides, plays a role in vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P28222
- Molecular Weight:
- 43567.535 Da
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor signaling protein activity
- Specific Function:
- Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. This receptor binds epinephrine and norepinephrine with approximately equal affinity. Mediates Ras activation through G(s)-alpha- and cAMP-mediated signaling.
- Gene Name:
- ADRB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08588
- Molecular Weight:
- 51322.1 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.14 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21728
- Molecular Weight:
- 49292.765 Da
References
- Passie T, Halpern JH, Stichtenoth DO, Emrich HM, Hintzen A: The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2008 Winter;14(4):295-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. [19040555 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Promotes cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- DRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P35462
- Molecular Weight:
- 44224.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.027 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Sh3 domain binding
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Its activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Modulates the circadian rhythm of contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of NPAS2 in the retinal ganglion cells (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- DRD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P21917
- Molecular Weight:
- 48359.86 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.056 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
- Gene Name:
- HRH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35367
- Molecular Weight:
- 55783.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 1.54 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21342 |
References
- Nichols DE, Frescas S, Marona-Lewicka D, Kurrasch-Orbaugh DM: Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD). J Med Chem. 2002 Sep 12;45(19):4344-9. [12213075 ]