Haloperidol (T3D2576)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-05 03:35:09 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:43 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2576 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Haloperidol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | A phenyl-piperidinyl-butyrophenone that is used primarily to treat schizophrenia and other psychoses. It is also used in schizoaffective disorder, delusional disorders, ballism, and tourette syndrome (a drug of choice) and occasionally as adjunctive therapy in mental retardation and the chorea of huntington disease. It is a potent antiemetic and is used in the treatment of intractable hiccups. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p279) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
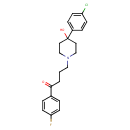
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C21H23ClFNO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 375.864 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 375.140 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 52-86-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 4-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)butan-1-one | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | haloperidol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC1(CCN(CCCC(=O)C2=CC=C(F)C=C2)CC1)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C21H23ClFNO2/c22-18-7-5-17(6-8-18)21(26)11-14-24(15-12-21)13-1-2-20(25)16-3-9-19(23)10-4-16/h3-10,26H,1-2,11-15H2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=LNEPOXFFQSENCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alkyl-phenylketones. These are aromatic compounds containing a ketone substituted by one alkyl group, and a phenyl group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Alkyl-phenylketones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White to faintly yellowish, amorphous or micro-crystalline powder (2). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation, Oral (60%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The precise mechanism whereby the therapeutic effects of haloperidol are produced is not known, but the drug appears to depress the CNS at the subcortical level of the brain, midbrain, and brain stem reticular formation. Haloperidol seems to inhibit the ascending reticular activating system of the brain stem (possibly through the caudate nucleus), thereby interrupting the impulse between the diencephalon and the cortex. The drug may antagonize the actions of glutamic acid within the extrapyramidal system, and inhibitions of catecholamine receptors may also contribute to haloperidol's mechanism of action. Haloperidol may also inhibit the reuptake of various neurotransmitters in the midbrain, and appears to have a strong central antidopaminergic and weak central anticholinergic activity. The drug produces catalepsy and inhibits spontaneous motor activity and conditioned avoidance behaviours in animals. The exact mechanism of antiemetic action of haloperidol has also not been fully determined, but the drug has been shown to directly affect the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) through the blocking of dopamine receptors in the CTZ. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Haloperidol is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but first-pass hepatic metabolism decreases oral bioavailability to 40 to 75%. Serum concentration peaks 0.5 to 4 hours after an oral dose. Following administration of haloperidol, the drug is distributed mainly into the liver, with lower concentrations being distributed into the brain, lung, kidneys, spleen, and heart. Although the exact metabolic fate has not been clearly established, it appears that haloperidol is principally metabolized in the liver. The drug appears to be metabolized principally by oxidative N-dealkylation of the piperidine nitrogen to form fluorophenylcarbonic acids and piperidine metabolites (which appear to be inactive), and by reduction of the butyrophenone carbonyl to the carbinol, forming hydroxyhaloperidol. Limited data suggest that the reduced metabolite, hydroxyhaloperidol, has some pharmacologic activity, although its activity appears to be less than that of haloperidol. Urinary metabolites include p-fluorophenaceturic acid, beta-p-fluorobenzoylpropionic acid, and several unidentified acids (3, 4, 3). Half Life: 3 weeks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 128 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) LD50: 71 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) LD50: 90 mg/kg (Oral, Dog) LD50: 165 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For the management of psychotic disorders (eg. schizophrenia) and delirium, as well as to control tics and vocal utterances of Tourette's syndrome (Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome). Also used for the treatment of severe behavioural problems in children with disrubtive behaviour disorder or ADHD (attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder). Haloperidol has been used in the prevention and control of severe nausea and vomiting. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Tachycardia, hypotension, and hypertension; Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) such as akathisia, or dystonia; impaired liver function and/or jaundice have been reported. Maculopapular and acneiform skin reactions and isolated cases of photosensitivity and loss of hair.Laryngospasm, bronchospasm, cataracts, retinopathy and visual disturbances; lactation, breast engorgement, mastalgia, menstrual irregularities, gynecomastia, impotence, increased libido, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia and hyponatremia (RxList, A308). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | LD50=165 mg/kg (rats, oral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Since there is no specific antidote, treatment is primarily supportive. A patent airway must be established by use of an oropharyngeal airway or endotracheal tube or, in prolonged cases of coma, by tracheostomy. Respiratory depression may be counteracted by artificial respiration and mechanical respirators. Hypotension and circulatory collapse may be counteracted by use of intravenous fluids, plasma, or concentrated albumin, and vasopressor agents such as metaraminol, phenylephrine and norepinephrine. Epinephrine should not be used. In case of severe extrapyramidal reactions, anti-Parkinson medication should be administered. ECG and vital signs should be monitored especially for signs of Q-T prolongation or dysrhythmias and monitoring should continue until the ECG is normal. Severe arrhythmias should be treated with appropriate anti-arrhythmic measures. (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00502 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14645 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 3559 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 3438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C01814 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 5613 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Haloperidol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Haloperidol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Sh3 domain binding
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor responsible for neuronal signaling in the mesolimbic system of the brain, an area of the brain that regulates emotion and complex behavior. Its activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Modulates the circadian rhythm of contrast sensitivity by regulating the rhythmic expression of NPAS2 in the retinal ganglion cells (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- DRD4
- Uniprot ID:
- P21917
- Molecular Weight:
- 48359.86 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.0013 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.005 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.006 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.0065 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| AC50 | 0.01 uM | NVS_GPCR_hDRD4.4 | Novascreen |
References
- Perrone R, Berardi F, Colabufo NA, Leopoldo M, Tortorella V: N-[2-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-3-methoxybenzamide: a potent and selective dopamine D4 ligand. J Med Chem. 1998 Nov 19;41(24):4903-9. [9822559 ]
- Zhang X, Hodgetts K, Rachwal S, Zhao H, Wasley JW, Craven K, Brodbeck R, Kieltyka A, Hoffman D, Bacolod MD, Girard B, Tran J, Thurkauf A: trans-1-[(2-Phenylcyclopropyl)methyl]-4-arylpiperazines: mixed dopamine D(2)/D(4) receptor antagonists as potential antipsychotic agents. J Med Chem. 2000 Oct 19;43(21):3923-32. [11052797 ]
- Hrib NJ, Jurcak JG, Bregna DE, Burgher KL, Hartman HB, Kafka S, Kerman LL, Kongsamut S, Roehr JE, Szewczak MR, Woods-Kettelberger AT, Corbett R: Structure-activity relationships of a series of novel (piperazinylbutyl)thiazolidinone antipsychotic agents related to 3-[4-[4-(6-fluorobenzo[b]thien-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-2,5,5- trimethyl-4-thiazolidinone maleate. J Med Chem. 1996 Sep 27;39(20):4044-57. [8831770 ]
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.004 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.0041 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.0049 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.55 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| AC50 | 0.02 uM | NVS_GPCR_hDRD2s | Novascreen |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Osinski MA, Uchic ME, Seifert T, Shaughnessy TK, Miller LN, Nakane M, Cox BF, Brioni JD, Moreland RB: Dopamine D2, but not D4, receptor agonists are emetogenic in ferrets. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005 May;81(1):211-9. [15894081 ]
- Bustillo J, Barrow R, Paz R, Tang J, Seraji-Bozorgzad N, Moore GJ, Bolognani F, Lauriello J, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Galloway MP: Long-term treatment of rats with haloperidol: lack of an effect on brain N-acetyl aspartate levels. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Apr;31(4):751-6. [16132064 ]
- Ishiwata K, Oda K, Sakata M, Kimura Y, Kawamura K, Oda K, Sasaki T, Naganawa M, Chihara K, Okubo Y, Ishii K: A feasibility study of [11C]SA4503-PET for evaluating sigmal receptor occupancy by neuroleptics: the binding of haloperidol to sigma1 and dopamine D2-like receptors. Ann Nucl Med. 2006 Oct;20(8):569-73. [17134027 ]
- Zhang X, Hodgetts K, Rachwal S, Zhao H, Wasley JW, Craven K, Brodbeck R, Kieltyka A, Hoffman D, Bacolod MD, Girard B, Tran J, Thurkauf A: trans-1-[(2-Phenylcyclopropyl)methyl]-4-arylpiperazines: mixed dopamine D(2)/D(4) receptor antagonists as potential antipsychotic agents. J Med Chem. 2000 Oct 19;43(21):3923-32. [11052797 ]
- Perrone R, Berardi F, Colabufo NA, Leopoldo M, Tortorella V: N-[2-[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-3-methoxybenzamide: a potent and selective dopamine D4 ligand. J Med Chem. 1998 Nov 19;41(24):4903-9. [9822559 ]
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- Sun H, Zhu L, Yang H, Qian W, Guo L, Zhou S, Gao B, Li Z, Zhou Y, Jiang H, Chen K, Zhen X, Liu H: Asymmetric total synthesis and identification of tetrahydroprotoberberine derivatives as new antipsychotic agents possessing a dopamine D(1), D(2) and serotonin 5-HT(1A) multi-action profile. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Feb 15;21(4):856-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.12.016. Epub 2012 Dec 21. [23332346 ]
- Kapur S, McClelland RA, VanderSpek SC, Wadenberg ML, Baker G, Nobrega J, Zipursky RB, Seeman P: Increasing D2 affinity results in the loss of clozapine's atypical antipsychotic action. Neuroreport. 2002 May 7;13(6):831-5. [11997696 ]
- Arakawa R, Okumura M, Ito H, Takano A, Takahashi H, Takano H, Maeda J, Okubo Y, Suhara T: Positron emission tomography measurement of dopamine D(2) receptor occupancy in the pituitary and cerebral cortex: relation to antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010 Sep;71(9):1131-7. doi: 10.4088/JCP.08m04307yel. Epub 2010 Feb 23. [20361897 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21728
- Molecular Weight:
- 49292.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.02 uM | NVS_GPCR_hDRD1 | Novascreen |
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Theisen FM, Haberhausen M, Firnges MA, Gregory P, Reinders JH, Remschmidt H, Hebebrand J, Antel J: No evidence for binding of clozapine, olanzapine and/or haloperidol to selected receptors involved in body weight regulation. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007 Aug;7(4):275-81. Epub 2006 Sep 19. [16983399 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization
- Specific Function:
- Pore-forming (alpha) subunit of voltage-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel. Channel properties are modulated by cAMP and subunit assembly. Mediates the rapidly activating component of the delayed rectifying potassium current in heart (IKr). Isoforms USO have no channel activity by themself, but modulates channel characteristics by forming heterotetramers with other isoforms which are retained intracellularly and undergo ubiquitin-dependent degradation.
- Gene Name:
- KCNH2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12809
- Molecular Weight:
- 126653.52 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.028 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.0281 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.03 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.0302 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.032 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.23 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 1.1 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 1.4 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Rajamani R, Tounge BA, Li J, Reynolds CH: A two-state homology model of the hERG K+ channel: application to ligand binding. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Mar 15;15(6):1737-41. [15745831 ]
- Cavalli A, Poluzzi E, De Ponti F, Recanatini M: Toward a pharmacophore for drugs inducing the long QT syndrome: insights from a CoMFA study of HERG K(+) channel blockers. J Med Chem. 2002 Aug 29;45(18):3844-53. [12190308 ]
- Keseru GM: Prediction of hERG potassium channel affinity by traditional and hologram qSAR methods. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Aug 18;13(16):2773-5. [12873512 ]
- Tobita M, Nishikawa T, Nagashima R: A discriminant model constructed by the support vector machine method for HERG potassium channel inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2886-90. [15911273 ]
- Jia L, Sun H: Support vector machines classification of hERG liabilities based on atom types. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jun 1;16(11):6252-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.028. Epub 2008 Apr 16. [18448342 ]
- Pearlstein RA, Vaz RJ, Kang J, Chen XL, Preobrazhenskaya M, Shchekotikhin AE, Korolev AM, Lysenkova LN, Miroshnikova OV, Hendrix J, Rampe D: Characterization of HERG potassium channel inhibition using CoMSiA 3D QSAR and homology modeling approaches. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 May 19;13(10):1829-35. [12729675 ]
- Liu T, Lin Y, Wen X, Jorissen RN, Gilson MK: BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D198-201. Epub 2006 Dec 1. [17145705 ]
- Sams AG, Larsen K, Mikkelsen GK, Hentzer M, Christoffersen CT, Jensen KG, Frederiksen K, Bang-Andersen B: Hit-to-lead investigation of a series of novel combined dopamine D2 and muscarinic M1 receptor ligands with putative antipsychotic and pro-cognitive potential. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Aug 1;22(15):5134-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.05.048. Epub 2012 May 18. [22677319 ]
- Du LP, Tsai KC, Li MY, You QD, Xia L: The pharmacophore hypotheses of I(Kr) potassium channel blockers: novel class III antiarrhythmic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 20;14(18):4771-7. [15324906 ]
- General Function:
- Opioid receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Functions in lipid transport from the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in a wide array of cellular functions probably through regulation of the biogenesis of lipid microdomains at the plasma membrane. Involved in the regulation of different receptors it plays a role in BDNF signaling and EGF signaling. Also regulates ion channels like the potassium channel and could modulate neurotransmitter release. Plays a role in calcium signaling through modulation together with ANK2 of the ITP3R-dependent calcium efflux at the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in several other cell functions including proliferation, survival and death. Originally identified for its ability to bind various psychoactive drugs it is involved in learning processes, memory and mood alteration (PubMed:16472803, PubMed:9341151). Necessary for proper mitochondrial axonal transport in motor neurons, in particular the retrograde movement of mitochondria (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SIGMAR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99720
- Molecular Weight:
- 25127.52 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.0021 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.004 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.005 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.00564 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.008 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.017 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.021 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
| IC50 | 0.214 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Cazenave Gassiot A, Charton J, Girault-Mizzi S, Gilleron P, Debreu-Fontaine MA, Sergheraert C, Melnyk P: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of Tic-hydantoin derivatives as selective sigma1 ligands. Part 2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Nov 1;15(21):4828-32. [16140009 ]
- Charton J, Cazenave Gassiot A, Girault-Mizzi S, Debreu-Fontaine MA, Melnyk P, Sergheraert C: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of Tic-hydantoin derivatives as selective sigma1 ligands. Part 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Nov 1;15(21):4833-7. [16140011 ]
- Kimes AS, Wilson AA, Scheffel U, Campbell BG, London ED: Radiosynthesis, cerebral distribution, and binding of [125I]-1-(p-iodophenyl)-3-(1-adamantyl)guanidine, a ligand for sigma binding sites. J Med Chem. 1992 Dec 11;35(25):4683-9. [1469697 ]
- Wilson AA, Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Sonders MS, Weber E, Wagner HN Jr: Radiosynthesis of sigma receptor ligands for positron emission tomography: 11C- and 18F-labeled guanidines. J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1867-70. [1648140 ]
- Perrone R, Berardi F, Colabufo NA, Leopoldo M, Tortorella V, Fiorentini F, Olgiati V, Ghiglieri A, Govoni S: High affinity and selectivity on 5-HT1A receptor of 1-aryl-4-[1-tetralin)alkyl]piperazines. 2. J Med Chem. 1995 Mar 17;38(6):942-9. [7699710 ]
- Germain AR, Carmody LC, Nag PP, Morgan B, Verplank L, Fernandez C, Donckele E, Feng Y, Perez JR, Dandapani S, Palmer M, Lander ES, Gupta PB, Schreiber SL, Munoz B: Cinnamides as selective small-molecule inhibitors of a cellular model of breast cancer stem cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Mar 15;23(6):1834-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.01.025. Epub 2013 Jan 16. [23403082 ]
- Myers AM, Charifson PS, Owens CE, Kula NS, McPhail AT, Baldessarini RJ, Booth RG, Wyrick SD: Conformational analysis, pharmacophore identification, and comparative molecular field analysis of ligands for the neuromodulatory sigma 3 receptor. J Med Chem. 1994 Nov 25;37(24):4109-17. [7990111 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Promotes cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- DRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P35462
- Molecular Weight:
- 44224.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.01 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Leysen JE, Janssen PM, Megens AA, Schotte A: Risperidone: a novel antipsychotic with balanced serotonin-dopamine antagonism, receptor occupancy profile, and pharmacologic activity. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994 May;55 Suppl:5-12. [7520908 ]
- Tuppurainen H, Kuikka JT, Viinamaki H, Husso M, Tiihonen J: Dopamine D2/3 receptor binding potential and occupancy in midbrain and temporal cortex by haloperidol, olanzapine and clozapine. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009 Aug;63(4):529-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2009.01982.x. Epub 2009 May 22. [19496999 ]
- Tadori Y, Forbes RA, McQuade RD, Kikuchi T: Characterization of aripiprazole partial agonist activity at human dopamine D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Nov 12;597(1-3):27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Sep 20. [18831971 ]
- Kessler RM, Ansari MS, Riccardi P, Li R, Jayathilake K, Dawant B, Meltzer HY: Occupancy of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors by olanzapine and haloperidol. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Dec;30(12):2283-9. [16123775 ]
- Malmberg, Mikaels, Mohell N: Agonist and inverse agonist activity at the dopamine D3 receptor measured by guanosine 5'--gamma-thio-triphosphate--35S- binding. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Apr;285(1):119-26. [9536001 ]
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. In concert with DAPK1 at extrasynaptic sites, acts as a central mediator for stroke damage. Its phosphorylation at Ser-1303 by DAPK1 enhances synaptic NMDA receptor channel activity inducing injurious Ca2+ influx through them, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13224
- Molecular Weight:
- 166365.885 Da
References
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- Hattori K, Uchino S, Isosaka T, Maekawa M, Iyo M, Sato T, Kohsaka S, Yagi T, Yuasa S: Fyn is required for haloperidol-induced catalepsy in mice. J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7129-35. Epub 2006 Jan 10. [16407246 ]
- Zhuravliova E, Barbakadze T, Natsvlishvili N, Mikeladze DG: Haloperidol induces neurotoxicity by the NMDA receptor downstream signaling pathway, alternative from glutamate excitotoxicity. Neurochem Int. 2007 Jun;50(7-8):976-82. Epub 2006 Nov 7. [17092607 ]
- Gu WH, Yang S, Shi WX, Zhen XC, Jin GZ: Effects of (-)-stepholidine on NMDA receptors: comparison with haloperidol and clozapine. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Jul;28(7):953-8. [17588330 ]
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.288 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Leysen JE, Janssen PM, Megens AA, Schotte A: Risperidone: a novel antipsychotic with balanced serotonin-dopamine antagonism, receptor occupancy profile, and pharmacologic activity. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994 May;55 Suppl:5-12. [7520908 ]
- Hrib NJ, Jurcak JG, Bregna DE, Burgher KL, Hartman HB, Kafka S, Kerman LL, Kongsamut S, Roehr JE, Szewczak MR, Woods-Kettelberger AT, Corbett R: Structure-activity relationships of a series of novel (piperazinylbutyl)thiazolidinone antipsychotic agents related to 3-[4-[4-(6-fluorobenzo[b]thien-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]butyl]-2,5,5- trimethyl-4-thiazolidinone maleate. J Med Chem. 1996 Sep 27;39(20):4044-57. [8831770 ]
- General Function:
- Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase c activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11229
- Molecular Weight:
- 51420.375 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 5.5 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Liao Y, DeBoer P, Meier E, Wikstrom H: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of triflate-substituted analogues of clozapine: identification of a novel atypical neuroleptic. J Med Chem. 1997 Dec 5;40(25):4146-53. [9406603 ]
- Liao Y, Venhuis BJ, Rodenhuis N, Timmerman W, Wikstrom H, Meier E, Bartoszyk GD, Bottcher H, Seyfried CA, Sundell S: New (sulfonyloxy)piperazinyldibenzazepines as potential atypical antipsychotics: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation. J Med Chem. 1999 Jun 17;42(12):2235-44. [10377229 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 1.5 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Taverne T, Diouf O, Depreux P, Poupaert JH, Lesieur D, Guardiola-Lemaitre B, Renard P, Rettori MC, Caignard DH, Pfeiffer B: Novel benzothiazolin-2-one and benzoxazin-3-one arylpiperazine derivatives with mixed 5HT1A/D2 affinity as potential atypical antipsychotics. J Med Chem. 1998 Jun 4;41(12):2010-8. [9622542 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | >10 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Taverne T, Diouf O, Depreux P, Poupaert JH, Lesieur D, Guardiola-Lemaitre B, Renard P, Rettori MC, Caignard DH, Pfeiffer B: Novel benzothiazolin-2-one and benzoxazin-3-one arylpiperazine derivatives with mixed 5HT1A/D2 affinity as potential atypical antipsychotics. J Med Chem. 1998 Jun 4;41(12):2010-8. [9622542 ]
- General Function:
- Neuropeptide receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for melanin-concentrating hormone, coupled to both G proteins that inhibit adenylyl cyclase and G proteins that activate phosphoinositide hydrolysis.
- Gene Name:
- MCHR1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99705
- Molecular Weight:
- 45962.185 Da
References
- Theisen FM, Haberhausen M, Firnges MA, Gregory P, Reinders JH, Remschmidt H, Hebebrand J, Antel J: No evidence for binding of clozapine, olanzapine and/or haloperidol to selected receptors involved in body weight regulation. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007 Aug;7(4):275-81. Epub 2006 Sep 19. [16983399 ]
- General Function:
- Xenobiotic-transporting atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- Energy-dependent efflux pump responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells.
- Gene Name:
- ABCB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08183
- Molecular Weight:
- 141477.255 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 5.3 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Pajeva IK, Wiese M: Pharmacophore model of drugs involved in P-glycoprotein multidrug resistance: explanation of structural variety (hypothesis). J Med Chem. 2002 Dec 19;45(26):5671-86. [12477351 ]
- General Function:
- Secondary active organic cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Translocates a broad array of organic cations with various structures and molecular weights including the model compounds 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP), the endogenous compounds choline, guanidine, histamine, epinephrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, and the drugs quinine, and metformin. The transport of organic cations is inhibited by a broad array of compounds like tetramethylammonium (TMA), cocaine, lidocaine, NMDA receptor antagonists, atropine, prazosin, cimetidine, TEA and NMN, guanidine, cimetidine, choline, procainamide, quinine, tetrabutylammonium, and tetrapentylammonium. Translocates organic cations in an electrogenic and pH-independent manner. Translocates organic cations across the plasma membrane in both directions. Transports the polyamines spermine and spermidine. Transports pramipexole across the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubular epithelial cells. The choline transport is activated by MMTS. Regulated by various intracellular signaling pathways including inhibition by protein kinase A activation, and endogenously activation by the calmodulin complex, the calmodulin-dependent kinase II and LCK tyrosine kinase.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O15245
- Molecular Weight:
- 61153.345 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 141.9 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 21398 |
References
- Ahlin G, Karlsson J, Pedersen JM, Gustavsson L, Larsson R, Matsson P, Norinder U, Bergstrom CA, Artursson P: Structural requirements for drug inhibition of the liver specific human organic cation transport protein 1. J Med Chem. 2008 Oct 9;51(19):5932-42. doi: 10.1021/jm8003152. Epub 2008 Sep 13. [18788725 ]
- General Function:
- Monoamine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the ATP-dependent vesicular transport of biogenic amine neurotransmitters. Pumps cytosolic monoamines including dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine into synaptic vesicles. Requisite for vesicular amine storage prior to secretion via exocytosis.
- Gene Name:
- SLC18A2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05940
- Molecular Weight:
- 55712.075 Da
References
- Gonzalez AM, Walther D, Pazos A, Uhl GR: Synaptic vesicular monoamine transporter expression: distribution and pharmacologic profile. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Mar;22(1-4):219-26. [7912402 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- HTR7
- Uniprot ID:
- P34969
- Molecular Weight:
- 53554.43 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.63 uM | NVS_GPCR_h5HT7 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Norepinephrine:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Amine transporter. Terminates the action of noradrenaline by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P23975
- Molecular Weight:
- 69331.42 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.15 uM | NVS_TR_hNET | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcription factor. Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Has a preference for poly-unsaturated fatty acids, such as gamma-linoleic acid and eicosapentanoic acid. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to promoter elements of target genes. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the acyl-CoA oxidase gene. Decreases expression of NPC1L1 once activated by a ligand.
- Gene Name:
- PPARD
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03181
- Molecular Weight:
- 49902.99 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.61 uM | ATG_PPARd_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P18825
- Molecular Weight:
- 49521.585 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.10 uM | NVS_GPCR_hAdra2C | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
- Gene Name:
- HRH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35367
- Molecular Weight:
- 55783.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.52 uM | NVS_GPCR_hH1 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Monoamine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Amine transporter. Terminates the action of dopamine by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01959
- Molecular Weight:
- 68494.255 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.81 uM | NVS_TR_hDAT | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.03 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated calcium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for endogenous opioids such as beta-endorphin and endomorphin. Receptor for natural and synthetic opioids including morphine, heroin, DAMGO, fentanyl, etorphine, buprenorphin and methadone. Agonist binding to the receptor induces coupling to an inactive GDP-bound heterotrimeric G-protein complex and subsequent exchange of GDP for GTP in the G-protein alpha subunit leading to dissociation of the G-protein complex with the free GTP-bound G-protein alpha and the G-protein beta-gamma dimer activating downstream cellular effectors. The agonist- and cell type-specific activity is predominantly coupled to pertussis toxin-sensitive G(i) and G(o) G alpha proteins, GNAI1, GNAI2, GNAI3 and GNAO1 isoforms Alpha-1 and Alpha-2, and to a lesser extend to pertussis toxin-insensitive G alpha proteins GNAZ and GNA15. They mediate an array of downstream cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity and both N-type and L-type calcium channels, activation of inward rectifying potassium channels, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phospholipase C (PLC), phosphoinositide/protein kinase (PKC), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and regulation of NF-kappa-B. Also couples to adenylate cyclase stimulatory G alpha proteins. The selective temporal coupling to G-proteins and subsequent signaling can be regulated by RGSZ proteins, such as RGS9, RGS17 and RGS4. Phosphorylation by members of the GPRK subfamily of Ser/Thr protein kinases and association with beta-arrestins is involved in short-term receptor desensitization. Beta-arrestins associate with the GPRK-phosphorylated receptor and uncouple it from the G-protein thus terminating signal transduction. The phosphorylated receptor is internalized through endocytosis via clathrin-coated pits which involves beta-arrestins. The activation of the ERK pathway occurs either in a G-protein-dependent or a beta-arrestin-dependent manner and is regulated by agonist-specific receptor phosphorylation. Acts as a class A G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) which dissociates from beta-arrestin at or near the plasma membrane and undergoes rapid recycling. Receptor down-regulation pathways are varying with the agonist and occur dependent or independent of G-protein coupling. Endogenous ligands induce rapid desensitization, endocytosis and recycling whereas morphine induces only low desensitization and endocytosis. Heterooligomerization with other GPCRs can modulate agonist binding, signaling and trafficking properties. Involved in neurogenesis. Isoform 12 couples to GNAS and is proposed to be involved in excitatory effects. Isoform 16 and isoform 17 do not bind agonists but may act through oligomerization with binding-competent OPRM1 isoforms and reduce their ligand binding activity.
- Gene Name:
- OPRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35372
- Molecular Weight:
- 44778.855 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.24 uM | NVS_GPCR_hOpiate_mu | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase c activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM5
- Uniprot ID:
- P08912
- Molecular Weight:
- 60073.205 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.86 uM | NVS_GPCR_hM5 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Serotonin transporter whose primary function in the central nervous system involves the regulation of serotonergic signaling via transport of serotonin molecules from the synaptic cleft back into the pre-synaptic terminal for re-utilization. Plays a key role in mediating regulation of the availability of serotonin to other receptors of serotonergic systems. Terminates the action of serotonin and recycles it in a sodium-dependent manner.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A4
- Uniprot ID:
- P31645
- Molecular Weight:
- 70324.165 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.96 uM | NVS_TR_hSERT | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Thioesterase binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08913
- Molecular Weight:
- 48956.275 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.51 uM | NVS_GPCR_hAdra2A | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]