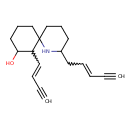
Histrionicotoxin (T3D2528)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 22:19:12 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:39 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2528 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Histrionicotoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Histrionicotoxin is a toxin found in poison dart frogs (genus Dendrobates). It is a potent non-competitive antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C19H25NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 283.408 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 283.194 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 34272-51-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 7-(but-1-en-3-yn-1-yl)-2-(pent-2-en-4-yn-1-yl)-1-azaspiro[5.5]undecan-8-ol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 7-(but-1-en-3-yn-1-yl)-2-(pent-2-en-4-yn-1-yl)-1-azaspiro[5.5]undecan-8-ol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC1CCCC2(CCCC(CC=CC#C)N2)C1C=CC#C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C19H25NO/c1-3-5-7-10-16-11-8-14-19(20-16)15-9-13-18(21)17(19)12-6-4-2/h1-2,5-7,12,16-18,20-21H,8-11,13-15H2/b7-5+,12-6+ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JBRYWENFVHQBGY-YTEPGLGFSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as histrionicotoxins. These are frog toxins structurally characterized by the presence of a dodecahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinolin-1-yl}ethanol moiety or a 2,7-disubstituted 1-azaspiro[5.5]undecan-8-ol moiety. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Histrionicotoxins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Histrionicotoxins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Injection (sting/bite) (2) ; inhalation (smoking) (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Histrionicotoxin is a potent non-competitive antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Histrionicotoxin is a toxin found in poison dart frogs (genus Dendrobates). (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Histrionicotoxin is neurotoxic. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Histrionicotoxin is neurotoxic. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 6437364 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C13683 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | C007948 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Histrionicotoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P02708
- Molecular Weight:
- 54545.235 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11230
- Molecular Weight:
- 56697.9 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRND
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07001
- Molecular Weight:
- 58894.55 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04844
- Molecular Weight:
- 54696.54 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNG
- Uniprot ID:
- P07510
- Molecular Weight:
- 57882.8 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding may induce an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane. In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA10
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9GZZ6
- Molecular Weight:
- 49704.295 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15822
- Molecular Weight:
- 59764.82 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32297
- Molecular Weight:
- 57479.54 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodium ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P43681
- Molecular Weight:
- 69956.47 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA5
- Uniprot ID:
- P30532
- Molecular Weight:
- 53053.965 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15825
- Molecular Weight:
- 56897.745 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Toxic substance binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P36544
- Molecular Weight:
- 56448.925 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Calcium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding induces a conformation change that leads to the opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma. May also regulate keratinocyte adhesion (PubMed:11021840).
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA9
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UGM1
- Molecular Weight:
- 54806.63 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodiun ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17787
- Molecular Weight:
- 57018.575 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05901
- Molecular Weight:
- 52728.215 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB4
- Uniprot ID:
- P30926
- Molecular Weight:
- 56378.985 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Histrionicotoxin. Last Updated 23 January 2009. [Link]