You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Tubocurarine (T3D3097)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-23 18:26:15 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:58 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3097 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Tubocurarine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Tubocurarine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a neuromuscular blocker and active ingredient in curare; plant based alkaloid of Menispermaceae. [PubChem]Tubocurarine, the chief alkaloid in tobacco products, binds stereo-selectively to nicotinic-cholinergic receptors at the autonomic ganglia, in the adrenal medulla, at neuromuscular junctions, and in the brain. Two types of central nervous system effects are believed to be the basis of Tubocurarine's positively reinforcing properties. A stimulating effect is exerted mainly in the cortex via the locus ceruleus and a reward effect is exerted in the limbic system. At low doses the stimulant effects predominate while at high doses the reward effects predominate. Intermittent intravenous administration of Tubocurarine activates neurohormonal pathways, releasing acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, vasopressin, beta-endorphin, growth hormone, and ACTH. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
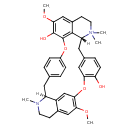
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C37H41N2O6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 609.731 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 609.296 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 6989-98-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (1S,16R)-9,21-dihydroxy-10,25-dimethoxy-15,15,30-trimethyl-7,23-dioxa-15,30-diazaheptacyclo[22.6.2.2³,⁶.1⁸,¹².1¹⁸,²².0²⁷,³¹.0¹⁶,³⁴]hexatriaconta-3,5,8(34),9,11,18(33),19,21,24,26,31,35-dodecaen-15-ium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | tubocurarine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12CC3=CC=C(OC4=C5C(CC[N+](C)(C)[C@]5([H])CC5=CC(OC6=C(OC)C=C(CCN1C)C2=C6)=C(O)C=C5)=CC(OC)=C4O)C=C3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C37H40N2O6/c1-38-14-12-24-19-32(42-4)33-21-27(24)28(38)16-22-6-9-26(10-7-22)44-37-35-25(20-34(43-5)36(37)41)13-15-39(2,3)29(35)17-23-8-11-30(40)31(18-23)45-33/h6-11,18-21,28-29H,12-17H2,1-5H3,(H-,40,41)/p+1/t28-,29+/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JFJZZMVDLULRGK-URLMMPGGSA-O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as diarylethers. These are organic compounds containing the dialkyl ether functional group, with the formula ROR', where R and R' are aryl groups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Ethers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Diarylethers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Injection (sting/bite) (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Tubocurarine is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Half Life: 1-2 hours | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Tubocurarine is a type of curare, a plant toxin known for its use as paralyzing arrow poison by South American indigenous people. It can be extracted from a variety of plants, including Strychnos toxifera and Chondrodendron tomentosum. (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Acute exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors can cause a cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Accumulation of ACh at motor nerves causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression at the neuromuscular junction. When this occurs symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, fasciculation, and paralysis can be seen. When there is an accumulation of ACh at autonomic ganglia this causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression in the sympathetic system. Symptoms associated with this are hypertension, and hypoglycemia. Overstimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system, due to accumulation of ACh, results in anxiety, headache, convulsions, ataxia, depression of respiration and circulation, tremor, general weakness, and potentially coma. When there is expression of muscarinic overstimulation due to excess acetylcholine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors symptoms of visual disturbances, tightness in chest, wheezing due to bronchoconstriction, increased bronchial secretions, increased salivation, lacrimation, sweating, peristalsis, and urination can occur. Certain reproductive effects in fertility, growth, and development for males and females have been linked specifically to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Most of the research on reproductive effects has been conducted on farmers working with pesticides and insecticdes in rural areas. In females menstrual cycle disturbances, longer pregnancies, spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and some developmental effects in offspring have been linked to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Prenatal exposure has been linked to impaired fetal growth and development. Neurotoxic effects have also been linked to poisoning with OP pesticides causing four neurotoxic effects in humans: cholinergic syndrome, intermediate syndrome, organophosphate-induced delayed polyneuropathy (OPIDP), and chronic organophosphate-induced neuropsychiatric disorder (COPIND). These syndromes result after acute and chronic exposure to OP pesticides. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Curare is a muscle relaxant and thus causes paraylsis. (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | If the compound has been ingested, rapid gastric lavage should be performed using 5% sodium bicarbonate. For skin contact, the skin should be washed with soap and water. If the compound has entered the eyes, they should be washed with large quantities of isotonic saline or water. In serious cases, atropine and/or pralidoxime should be administered. Anti-cholinergic drugs work to counteract the effects of excess acetylcholine and reactivate AChE. Atropine can be used as an antidote in conjunction with pralidoxime or other pyridinium oximes (such as trimedoxime or obidoxime), though the use of '-oximes' has been found to be of no benefit, or possibly harmful, in at least two meta-analyses. Atropine is a muscarinic antagonist, and thus blocks the action of acetylcholine peripherally. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB01199 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB15330 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 6000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1687 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 5778 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07547 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 9774 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Tubocurarine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Tubocurarine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. This receptor is a ligand-gated ion channel, which when activated causes fast, depolarizing responses in neurons. It is a cation-specific, but otherwise relatively nonselective, ion channel.
- Gene Name:
- HTR3A
- Uniprot ID:
- P46098
- Molecular Weight:
- 55279.835 Da
References
- Hefft S, Hulo S, Bertrand D, Muller D: Synaptic transmission at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal organotypic cultures and slices. J Physiol. 1999 Mar 15;515 ( Pt 3):769-76. [10066903 ]
- Yan D, White MM: Interaction of d-tubocurarine analogs with mutant 5-HT(3) receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2002 Sep;43(3):367-73. [12243766 ]
- Yan D, Meyer JK, White MM: Mapping residues in the ligand-binding domain of the 5-HT(3) receptor onto d-tubocurarine structure. Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;70(2):571-8. Epub 2006 May 24. [16723497 ]
- Peters JA, Malone HM, Lambert JJ: Antagonism of 5-HT3 receptor mediated currents in murine N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by (+)-tubocurarine. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 2;110(1-2):107-12. [1691468 ]
- Emerit MB, Riad M, Fattaccini CM, Hamon M: Characteristics of [14C]guanidinium accumulation in NG 108-15 cells exposed to serotonin 5-HT3 receptor ligands and substance P. J Neurochem. 1993 Jun;60(6):2059-67. [7684066 ]
- General Function:
- Serine hydrolase activity
- Specific Function:
- Terminates signal transduction at the neuromuscular junction by rapid hydrolysis of the acetylcholine released into the synaptic cleft. Role in neuronal apoptosis.
- Gene Name:
- ACHE
- Uniprot ID:
- P22303
- Molecular Weight:
- 67795.525 Da
References
- Radic Z, Taylor P: The influence of peripheral site ligands on the reaction of symmetric and chiral organophosphates with wildtype and mutant acetylcholinesterases. Chem Biol Interact. 1999 May 14;119-120:111-7. [10421444 ]
- Golicnik M, Fournier D, Stojan J: Acceleration of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase methanesulfonylation: peripheral ligand D-tubocurarine enhances the affinity for small methanesulfonylfluoride. Chem Biol Interact. 2002 Feb 20;139(2):145-57. [11823003 ]
- Radic Z, Taylor P: Peripheral site ligands accelerate inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by neutral organophosphates. J Appl Toxicol. 2001 Dec;21 Suppl 1:S13-4. [11920914 ]
- Gupta RC, Dettbarn WD: Potential of memantine, D-tubocurarine, and atropine in preventing acute toxic myopathy induced by organophosphate nerve agents: soman, sarin, tabun and VX. Neurotoxicology. 1992 Fall;13(3):649-61. [1475066 ]
- Bianchi DA, Hirschmann GS, Theoduloz C, Bracca AB, Kaufman TS: Synthesis of tricyclic analogs of stephaoxocanidine and their evaluation as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2711-5. [15878275 ]
- General Function:
- Toxic substance binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P36544
- Molecular Weight:
- 56448.925 Da
References
- Briggs CA, McKenna DG, Monteggia LM, Touma E, Roch JM, Arneric SP, Gopalakrishnan M, Sullivan JP: Gain of function mutation of the alpha7 nicotinic receptor: distinct pharmacology of the human alpha7V274T variant. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Feb 5;366(2-3):301-8. [10082212 ]
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P02708
- Molecular Weight:
- 54545.235 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11230
- Molecular Weight:
- 56697.9 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRND
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07001
- Molecular Weight:
- 58894.55 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04844
- Molecular Weight:
- 54696.54 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNG
- Uniprot ID:
- P07510
- Molecular Weight:
- 57882.8 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Monovalent cation:proton antiporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Solute transporter for tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, N-methylnicotinamide (NMN), metformin, creatinine, guanidine, procainamide, topotecan, estrone sulfate, acyclovir, ganciclovir and also the zwitterionic cephalosporin, cephalexin and cephradin. Seems to also play a role in the uptake of oxaliplatin (a new platinum anticancer agent). Able to transport paraquat (PQ or N,N-dimethyl-4-4'-bipiridinium); a widely used herbicid. Responsible for the secretion of cationic drugs across the brush border membranes.
- Gene Name:
- SLC47A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96FL8
- Molecular Weight:
- 61921.585 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 9.4 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50424714 |
References
- Wittwer MB, Zur AA, Khuri N, Kido Y, Kosaka A, Zhang X, Morrissey KM, Sali A, Huang Y, Giacomini KM: Discovery of potent, selective multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter 1 (MATE1, SLC47A1) inhibitors through prescription drug profiling and computational modeling. J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 14;56(3):781-95. doi: 10.1021/jm301302s. Epub 2013 Jan 22. [23241029 ]
- General Function:
- Drug transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Solute transporter for tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, N-methylnicotinamide, metformin, creatinine, guanidine, procainamide, topotecan, estrone sulfate, acyclovir, and ganciclovir. Responsible for the secretion of cationic drugs across the brush border membranes.
- Gene Name:
- SLC47A2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q86VL8
- Molecular Weight:
- 65083.915 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 55.5 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50424714 |
References
- Wittwer MB, Zur AA, Khuri N, Kido Y, Kosaka A, Zhang X, Morrissey KM, Sali A, Huang Y, Giacomini KM: Discovery of potent, selective multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter 1 (MATE1, SLC47A1) inhibitors through prescription drug profiling and computational modeling. J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 14;56(3):781-95. doi: 10.1021/jm301302s. Epub 2013 Jan 22. [23241029 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding may induce an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane. In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA10
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9GZZ6
- Molecular Weight:
- 49704.295 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15822
- Molecular Weight:
- 59764.82 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32297
- Molecular Weight:
- 57479.54 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodium ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P43681
- Molecular Weight:
- 69956.47 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA5
- Uniprot ID:
- P30532
- Molecular Weight:
- 53053.965 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15825
- Molecular Weight:
- 56897.745 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Calcium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding induces a conformation change that leads to the opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma. May also regulate keratinocyte adhesion (PubMed:11021840).
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA9
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UGM1
- Molecular Weight:
- 54806.63 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodiun ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17787
- Molecular Weight:
- 57018.575 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05901
- Molecular Weight:
- 52728.215 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB4
- Uniprot ID:
- P30926
- Molecular Weight:
- 56378.985 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Curare. Last Updated 9 June 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Quaternary ammonium group transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates tubular uptake of organic compounds from circulation. Mediates the influx of agmatine, dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), serotonin, choline, famotidine, ranitidine, histamin, creatinine, amantadine, memantine, acriflavine, 4-[4-(dimethylamino)-styryl]-N-methylpyridinium ASP, amiloride, metformin, N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, cisplatin and oxaliplatin. Cisplatin may develop a nephrotoxic action. Transport of creatinine is inhibited by fluoroquinolones such as DX-619 and LVFX. This transporter is a major determinant of the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin and may contribute to antitumor specificity.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A2
- Uniprot ID:
- O15244
- Molecular Weight:
- 62579.99 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 78.8 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50424714 |
References
- Wittwer MB, Zur AA, Khuri N, Kido Y, Kosaka A, Zhang X, Morrissey KM, Sali A, Huang Y, Giacomini KM: Discovery of potent, selective multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter 1 (MATE1, SLC47A1) inhibitors through prescription drug profiling and computational modeling. J Med Chem. 2013 Feb 14;56(3):781-95. doi: 10.1021/jm301302s. Epub 2013 Jan 22. [23241029 ]