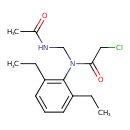
Amidochlor (T3D1086)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-06-18 21:54:33 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:06 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D1086 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Amidochlor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Widely used selective herbicides worldwide in corn, soybean and other crop cultures. Elevated concentrations of these herbicides and their degradation products have been detected in surface and groundwater. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C15H21ClN2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 296.792 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 296.129 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 40164-67-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 2-chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-N-(acetamidomethyl)acetamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 2-chloro-N-(2,6-diethylphenyl)-N-(acetamidomethyl)acetamide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCC1=CC=CC(CC)=C1N(CNC(C)=O)C(=O)CCl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H21ClN2O2/c1-4-12-7-6-8-13(5-2)15(12)18(14(20)9-16)10-17-11(3)19/h6-8H,4-5,9-10H2,1-3H3,(H,17,19) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=QTGVGIVRLSGTJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as anilides. These are organic heterocyclic compounds derived from oxoacids RkE(=O)l(OH)m (l not 0) by replacing an OH group by the NHPh group or derivative formed by ring substitution. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Benzenoids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Anilides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Anilides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Binds to nAChRs in nervous systems. It also causes endocrine disruption in humans by binding to and inhibiting the estrogen receptor. (3, 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Amidochlor is used as a herbicide. (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Amidochlor is neurotoxic. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 38407 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 35202 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Amidochlor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
References
- Taccone-Gallucci M, Manca-di-Villahermosa S, Battistini L, Stuffler RG, Tedesco M, Maccarrone M: N-3 PUFAs reduce oxidative stress in ESRD patients on maintenance HD by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase activity. Kidney Int. 2006 Apr;69(8):1450-4. [16531984 ]
- Luft S, Milki E, Glustrom E, Ampiah-Bonney R, O'Hara P. Binding of Organochloride and Pyrethroid Pesticides To Estrogen Receptors α and β: A Fluorescence Polarization Assay. Biophysical Journal 2009;96(3):444a.
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner (PubMed:20074560). Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
- Gene Name:
- ESR2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92731
- Molecular Weight:
- 59215.765 Da
References
- Taccone-Gallucci M, Manca-di-Villahermosa S, Battistini L, Stuffler RG, Tedesco M, Maccarrone M: N-3 PUFAs reduce oxidative stress in ESRD patients on maintenance HD by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase activity. Kidney Int. 2006 Apr;69(8):1450-4. [16531984 ]
- Luft S, Milki E, Glustrom E, Ampiah-Bonney R, O'Hara P. Binding of Organochloride and Pyrethroid Pesticides To Estrogen Receptors α and β: A Fluorescence Polarization Assay. Biophysical Journal 2009;96(3):444a.
- General Function:
- Receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding may induce an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane. In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA10
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9GZZ6
- Molecular Weight:
- 49704.295 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P32297
- Molecular Weight:
- 57479.54 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodium ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P43681
- Molecular Weight:
- 69956.47 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA5
- Uniprot ID:
- P30532
- Molecular Weight:
- 53053.965 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Acetylcholine-activated cation-selective channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15825
- Molecular Weight:
- 56897.745 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Toxic substance binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA7
- Uniprot ID:
- P36544
- Molecular Weight:
- 56448.925 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Calcium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding induces a conformation change that leads to the opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane (PubMed:11752216, PubMed:25282151). In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma. May also regulate keratinocyte adhesion (PubMed:11021840).
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA9
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UGM1
- Molecular Weight:
- 54806.63 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane permeable to sodiun ions.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17787
- Molecular Weight:
- 57018.575 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05901
- Molecular Weight:
- 52728.215 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNB4
- Uniprot ID:
- P30926
- Molecular Weight:
- 56378.985 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.