Esfenvalerate (T3D1036)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-06-18 17:03:35 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:05 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D1036 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Esfenvalerate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Esfenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide which is used on a wide range of pests such as moths, flies, beetles, and other insects. It is used on vegetable crops, tree fruit, and nut crops. It may be mixed with a wide variety of other types of pesticides such as carbamate compounds or organophosphates. Esfenvalerate has replaced the naturally occurring compound fenvalerate (to which it is almost identical) for use in the U.S. Much of the data for fenvalerate is applicable to the pesticide esfenvalerate because the two compounds contain the same components. The only differences in the two products are the relative proportions of the four separate constituents (isomers). Esfenvalerate has become the preferred compound because it requires lower applications rates than fenvalerate, is less chronically toxic, and is a more powerful insecticide. The compound contains a much higher percentage of the one insecticidally active isomer (84% for esfenvalerate and 22% for fenvalerate). A pyrethroid is a synthetic chemical compound similar to the natural chemical pyrethrins produced by the flowers of pyrethrums (Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium and C. coccineum). Pyrethroids are common in commercial products such as household insecticides and insect repellents. In the concentrations used in such products, they are generally harmless to human beings but can harm sensitive individuals. They are usually broken apart by sunlight and the atmosphere in one or two days, and do not significantly affect groundwater quality except for being toxic to fish. (7, 10, 11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
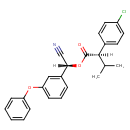
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C25H22ClNO3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 419.900 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 419.129 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 66230-04-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (R)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl (2R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutanoate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | (R)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl (2R)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methylbutanoate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@](OC(=O)[C@]([H])(C(C)C)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1)(C#N)C1=CC(OC2=CC=CC=C2)=CC=C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C25H22ClNO3/c1-17(2)24(18-11-13-20(26)14-12-18)25(28)30-23(16-27)19-7-6-10-22(15-19)29-21-8-4-3-5-9-21/h3-15,17,23-24H,1-2H3/t23-,24+/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=NYPJDWWKZLNGGM-BJKOFHAPSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrethroids. These are organic compounds similar to the pyrethrins. Some pyrethroids containing a chrysanthemic acid esterified with a cyclopentenone (pyrethrins), or with a phenoxybenzyl group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acid esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pyrethroids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | The pure compound exists as colorless crystals; the technical product as an amber liquid (11). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (8) ; oral (8) ; dermal (8) ; eye contact (8). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Both type I and type II pyrethroids exert their effect by prolonging the open phase of the sodium channel gates when a nerve cell is excited. They appear to bind to the membrane lipid phase in the immediate vicinity of the sodium channel, thus modifying the channel kinetics. This blocks the closing of the sodium gates in the nerves, and thus prolongs the return of the membrane potential to its resting state. The repetitive (sensory, motor) neuronal discharge and a prolonged negative afterpotential produces effects quite similar to those produced by DDT, leading to hyperactivity of the nervous system which can result in paralysis and/or death. Other mechanisms of action of pyrethroids include antagonism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated inhibition, modulation of nicotinic cholinergic transmission, enhancement of noradrenaline release, and actions on calcium ions. They also inhibit calium channels and Ca2+, Mg2+-ATPase. (3, 4, 8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Esfenvalerate is readily absorbed by the oral route, but less so dermally; absorbed deltamethrin is readily metabolized and excreted. The main urinary metabolites from the acid moiety are CPIA glucuronide, 3-hydroxy-CPIA (free and lactone), 2,3-hydroxy-CPIA glucuronide and 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-cis-2-butenedioic acid anhydride. The main urinary metabolite from the alcohol moiety is 3-(4'-hydroxyphenoxy)benzoic acid sulfate (16-24% of the administered radioactivity). Other metabolites included 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (free and glycine and glucuronide conjugates), 3-(4'-hydroxyphenoxy)benzoic acid (free and glucuronide) and 3-(2'-hydroxyphenoxy)benzoic acid (free and sulfate). (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 458 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (11) LD50: 2500 mg/kg (Dermal, Rabbit) (11) LC50: 2.93 mg/L (Inhalation, Rat) (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Pyrethroids are used as insecticides. (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | At high doses, signs of poisoning attributable to esfenvalerate include profuse salivation and pulmonary edema, clonic seizures, opisthotonos (i.e., the spine is bent forward such that a supine body rests on its head and heels), coma, and death. At lower doses, commonly observed effects include paresthesia and erythema. (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Following dermal exposure to esfenvalerate, feelings of numbness, itching, burning, stinging, tingling, or warmth may occur, that could last for a few hours. Dizziness, headache, nausea, muscle twitching, reduced energy, and changes in awareness can result from inhalation or ingestion of large amounts of esfenvalerate. Paralysis can occur after exposure. (8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Following oral exposure, the treatment is symptomatic and supportive and includes monitoring for the development of hypersensitivity reactions with respiratory distress. Provide adequate airway management when needed. Gastric decontamination is usually not required unless the pyrethrin product is combined with a hydrocarbon. Following inhalation exposure, move patient to fresh air. monitor for respiratory distress. If cough or difficulty breathing develops, evaluate for respiratory tract irritation, bronchitis, or pneumonitis. Administer oxygen and assist ventilation as required. Treat bronchospasm with inhaled beta2 agonist and oral or parenteral corticosteroids. In case of eye exposure, irrigate exposed eyes with copious amounts of room temperature water for at least 15 minutes. If irritation, pain, swelling, lacrimation, or photophobia persist, the patient should be seen in a health care facility. If the contamination occurs through dermal exposure, Remove contaminated clothing and wash exposed area thoroughly with soap and water. A physician may need to examine the area if irritation or pain persists. Vitamin E topical application is highly effective in relieving parenthesis. (12) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 5361514 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL492490 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 4514754 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 39346 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | 4-HYDROXYPHENYLACETATE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Esfenvalerate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | 7761 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D1036.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35498
- Molecular Weight:
- 228969.49 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Tetrodotoxin-resistant channel that mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. Plays a role in neuropathic pain mechanisms.
- Gene Name:
- SCN10A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y5Y9
- Molecular Weight:
- 220623.605 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel isoform. Also involved, with the contribution of the receptor tyrosine kinase NTRK2, in rapid BDNF-evoked neuronal depolarization.
- Gene Name:
- SCN11A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UI33
- Molecular Weight:
- 204919.66 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99250
- Molecular Weight:
- 227972.64 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN3A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY46
- Molecular Weight:
- 226291.905 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. This sodium channel may be present in both denervated and innervated skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- SCN4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35499
- Molecular Weight:
- 208059.175 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in sa node cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential. Channel inactivation is regulated by intracellular calcium levels.
- Gene Name:
- SCN5A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14524
- Molecular Weight:
- 226937.475 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN7A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01118
- Molecular Weight:
- 193491.605 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. In macrophages and melanoma cells, isoform 5 may participate in the control of podosome and invadopodia formation.
- Gene Name:
- SCN8A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UQD0
- Molecular Weight:
- 225278.005 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na(+) channel isoform. Plays a role in pain mechanisms, especially in the development of inflammatory pain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN9A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15858
- Molecular Weight:
- 226370.175 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in purkinje myocyte action potential
- Specific Function:
- Crucial in the assembly, expression, and functional modulation of the heterotrimeric complex of the sodium channel. The subunit beta-1 can modulate multiple alpha subunit isoforms from brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. Its association with neurofascin may target the sodium channels to the nodes of Ranvier of developing axons and retain these channels at the nodes in mature myelinated axons.Isoform 2: Cell adhesion molecule that plays a critical role in neuronal migration and pathfinding during brain development. Stimulates neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- SCN1B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07699
- Molecular Weight:
- 24706.955 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Crucial in the assembly, expression, and functional modulation of the heterotrimeric complex of the sodium channel. The subunit beta-2 causes an increase in the plasma membrane surface area and in its folding into microvilli. Interacts with TNR may play a crucial role in clustering and regulation of activity of sodium channels at nodes of Ranvier (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN2B
- Uniprot ID:
- O60939
- Molecular Weight:
- 24325.69 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Modulates channel gating kinetics. Causes unique persistent sodium currents. Inactivates the sodium channel opening more slowly than the subunit beta-1. Its association with neurofascin may target the sodium channels to the nodes of Ranvier of developing axons and retain these channels at the nodes in mature myelinated axons (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN3B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY72
- Molecular Weight:
- 24702.08 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Modulates channel gating kinetics. Causes negative shifts in the voltage dependence of activation of certain alpha sodium channels, but does not affect the voltage dependence of inactivation. Modulates the suceptibility of the sodium channel to inhibition by toxic peptides from spider, scorpion, wasp and sea anemone venom.
- Gene Name:
- SCN4B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8IWT1
- Molecular Weight:
- 24968.755 Da
References
- Everts HB, Sundberg JP, Ong DE: Immunolocalization of retinoic acid biosynthesis systems in selected sites in rat. Exp Cell Res. 2005 Aug 15;308(2):309-19. [15950969 ]
- Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Doull J (eds) (1995). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2003). Toxicological profile for pyrethrins and pyrethroids. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Signal transducer activity
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of the calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2C1
- Uniprot ID:
- P98194
- Molecular Weight:
- 100576.42 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2C2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75185
- Molecular Weight:
- 103186.475 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Key regulator of striated muscle performance by acting as the major Ca(2+) ATPase responsible for the reuptake of cytosolic Ca(2+) into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O14983
- Molecular Weight:
- 110251.36 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- S100 protein binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Isoform 2 is involved in the regulation of the contraction/relaxation cycle.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P16615
- Molecular Weight:
- 114755.765 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium. Transports calcium ions from the cytosol into the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93084
- Molecular Weight:
- 113976.23 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Peptidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Responsible for the proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Cleaves at the N-terminus of the A-beta peptide sequence, between residues 671 and 672 of APP, leads to the generation and extracellular release of beta-cleaved soluble APP, and a corresponding cell-associated C-terminal fragment which is later released by gamma-secretase.
- Gene Name:
- BACE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P56817
- Molecular Weight:
- 55710.28 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.83 uM | NVS_ENZ_hBACE | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 7.50 uM | NVS_ENZ_hBACE | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Synthesizes the second messagers cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinate-adenine dinucleotide phosphate, the former a second messenger for glucose-induced insulin secretion. Also has cADPr hydrolase activity. Also moonlights as a receptor in cells of the immune system.
- Gene Name:
- CD38
- Uniprot ID:
- P28907
- Molecular Weight:
- 34328.145 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_SAg_CD38_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- CCL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P13500
- Molecular Weight:
- 11024.87 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_SAg_MCP1_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Cleaves collagens of types I, II, and III at one site in the helical domain. Also cleaves collagens of types VII and X. In case of HIV infection, interacts and cleaves the secreted viral Tat protein, leading to a decrease in neuronal Tat's mediated neurotoxicity.
- Gene Name:
- MMP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03956
- Molecular Weight:
- 54006.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_hDFCGF_MMP1_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Acts as a receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Plays a role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation. Mediates the proteolysis-independent signal transduction activation effects of U-PA. It is subject to negative-feedback regulation by U-PA which cleaves it into an inactive form.
- Gene Name:
- PLAUR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03405
- Molecular Weight:
- 36977.62 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_BE3C_uPAR_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.62 uM | ATG_PXR_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 2.92 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 4.60 uM | ATG_PXR_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 2.90 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Vitamin d3 25-hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It performs a variety of oxidation reactions (e.g. caffeine 8-oxidation, omeprazole sulphoxidation, midazolam 1'-hydroxylation and midazolam 4-hydroxylation) of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,8-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase. The enzyme also hydroxylates etoposide (PubMed:11159812). Catalyzes 4-beta-hydroxylation of cholesterol. May catalyze 25-hydroxylation of cholesterol in vitro (PubMed:21576599).
- Gene Name:
- CYP3A4
- Uniprot ID:
- P08684
- Molecular Weight:
- 57342.67 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.37 uM | CLZD_CYP3A4_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 8.10 uM | CLZD_CYP3A4_24 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for retinoic acid. Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone acetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and associate with the coactivators leading to transcriptional activation. RARA plays an essential role in the regulation of retinoic acid-induced germ cell development during spermatogenesis. Has a role in the survival of early spermatocytes at the beginning prophase of meiosis. In Sertoli cells, may promote the survival and development of early meiotic prophase spermatocytes. In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity). Regulates expression of target genes in a ligand-dependent manner by recruiting chromatin complexes containing KMT2E/MLL5. Mediates retinoic acid-induced granulopoiesis.
- Gene Name:
- RARA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10276
- Molecular Weight:
- 50770.805 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.70 uM | ATG_RARa_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 5.60 uM | ATG_RARa_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,4-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2B6
- Uniprot ID:
- P20813
- Molecular Weight:
- 56277.81 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.42 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 8.88 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_24 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 9.35 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Prostaglandin e receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. The subsequent raise in intracellular cAMP is responsible for the relaxing effect of this receptor on smooth muscle.
- Gene Name:
- PTGER2
- Uniprot ID:
- P43116
- Molecular Weight:
- 39759.945 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_LPS_PGE2_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Primary amine oxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Important in cell-cell recognition. Appears to function in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Interacts with integrin alpha-4/beta-1 (ITGA4/ITGB1) on leukocytes, and mediates both adhesion and signal transduction. The VCAM1/ITGA4/ITGB1 interaction may play a pathophysiologic role both in immune responses and in leukocyte emigration to sites of inflammation.
- Gene Name:
- VCAM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P19320
- Molecular Weight:
- 81275.43 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_4H_VCAM1_down | BioSeek |
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_3C_VCAM1_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid binding
- Specific Function:
- UDPGT is of major importance in the conjugation and subsequent elimination of potentially toxic xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This isoform glucuronidates bilirubin IX-alpha to form both the IX-alpha-C8 and IX-alpha-C12 monoconjugates and diconjugate. Is also able to catalyze the glucuronidation of 17beta-estradiol, 17alpha-ethinylestradiol, 1-hydroxypyrene, 4-methylumbelliferone, 1-naphthol, paranitrophenol, scopoletin, and umbelliferone. Isoform 2 lacks transferase activity but acts as a negative regulator of isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- UGT1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22309
- Molecular Weight:
- 59590.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.22 uM | CLZD_UGT1A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. This enzyme contributes to the wide pharmacokinetics variability of the metabolism of drugs such as S-warfarin, diclofenac, phenytoin, tolbutamide and losartan.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C9
- Uniprot ID:
- P11712
- Molecular Weight:
- 55627.365 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 6.05 uM | CLZD_CYP2C9_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for retinoic acid. Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5. In the absence of ligand, acts mainly as an activator of gene expression due to weak binding to corepressors. Required for limb bud development. In concert with RARA or RARB, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- RARG
- Uniprot ID:
- P13631
- Molecular Weight:
- 50341.405 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.15 uM | ATG_DR5_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TNFSF10/TRAIL. The adapter molecule FADD recruits caspase-8 to the activated receptor. The resulting death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation which initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases (aspartate-specific cysteine proteases) mediating apoptosis. Promotes the activation of NF-kappa-B. Essential for ER stress-induced apoptosis.
- Gene Name:
- TNFRSF10B
- Uniprot ID:
- O14763
- Molecular Weight:
- 47877.885 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.20 uM | ATG_DR5_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.38 uM | ATG_ERa_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 9.40 uM | ATG_ERa_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]